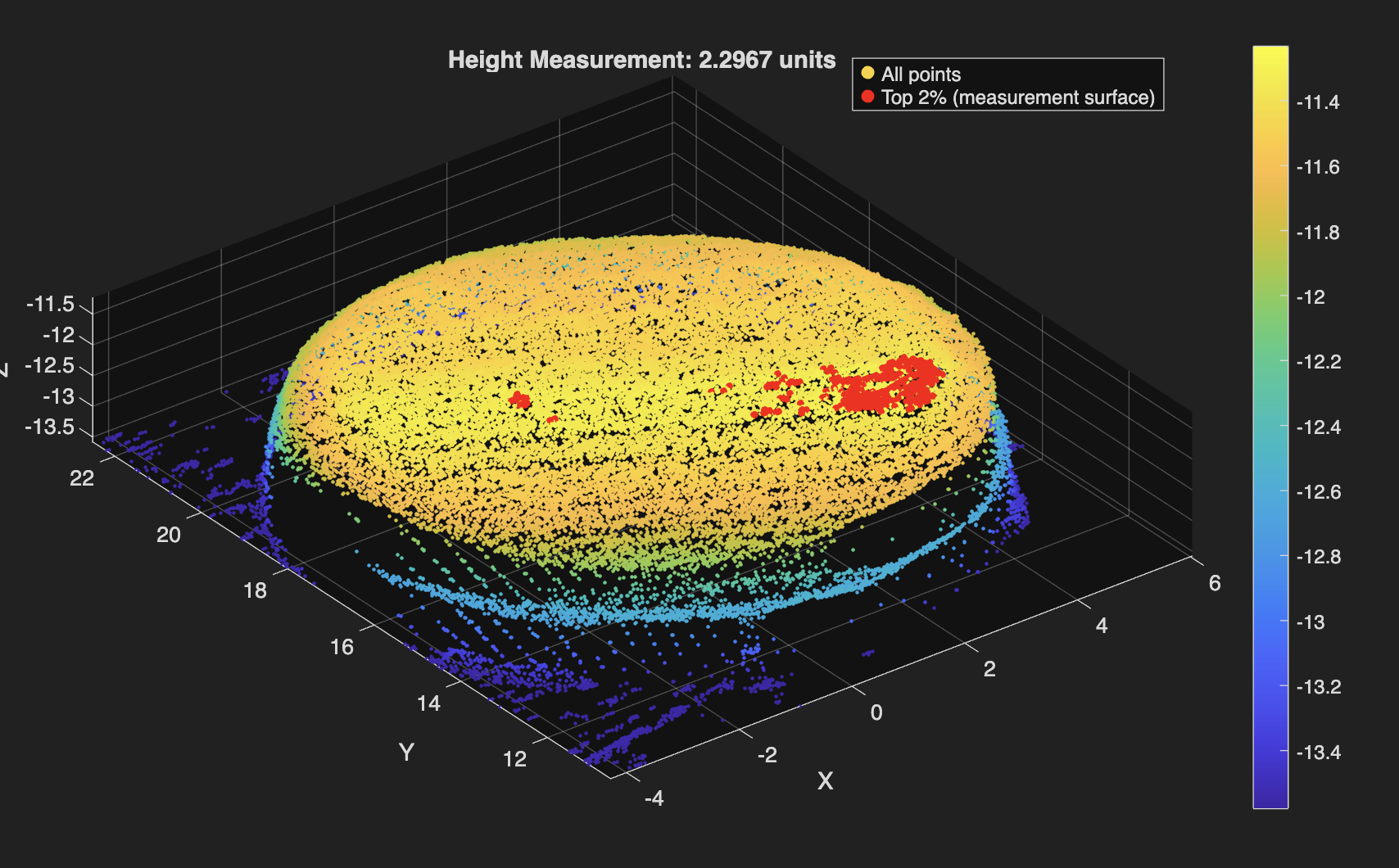
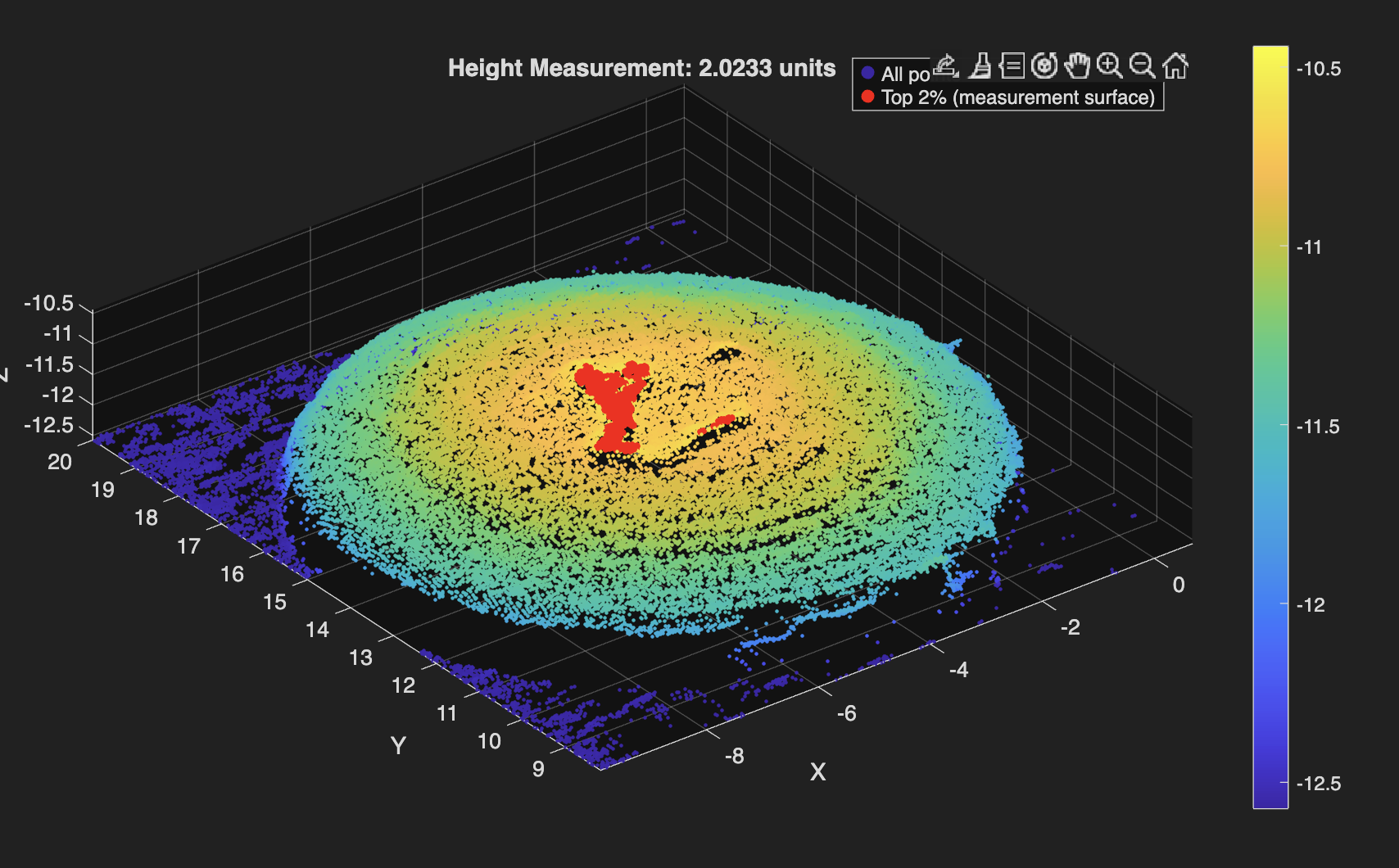
Laser Scanner Height Processing
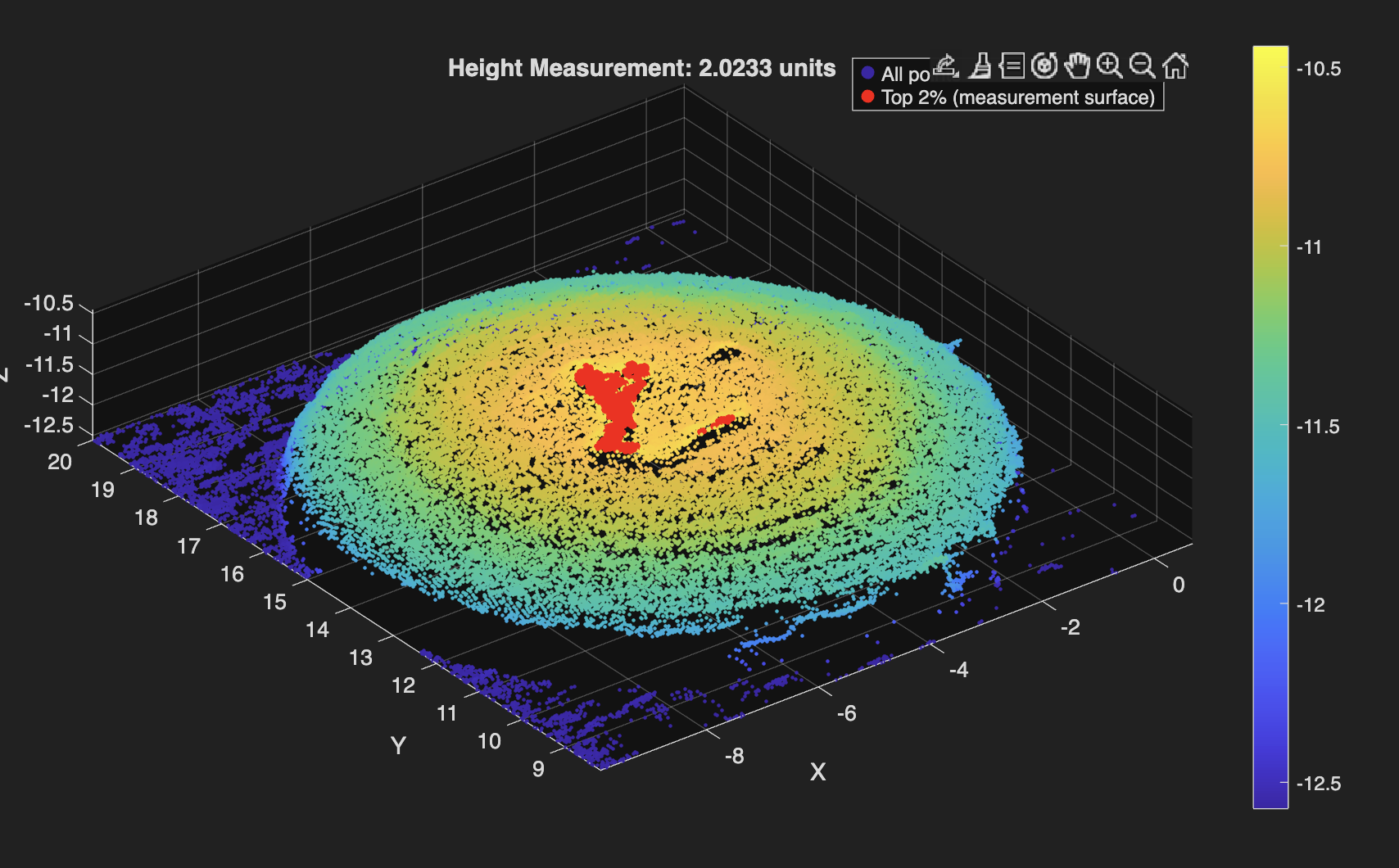
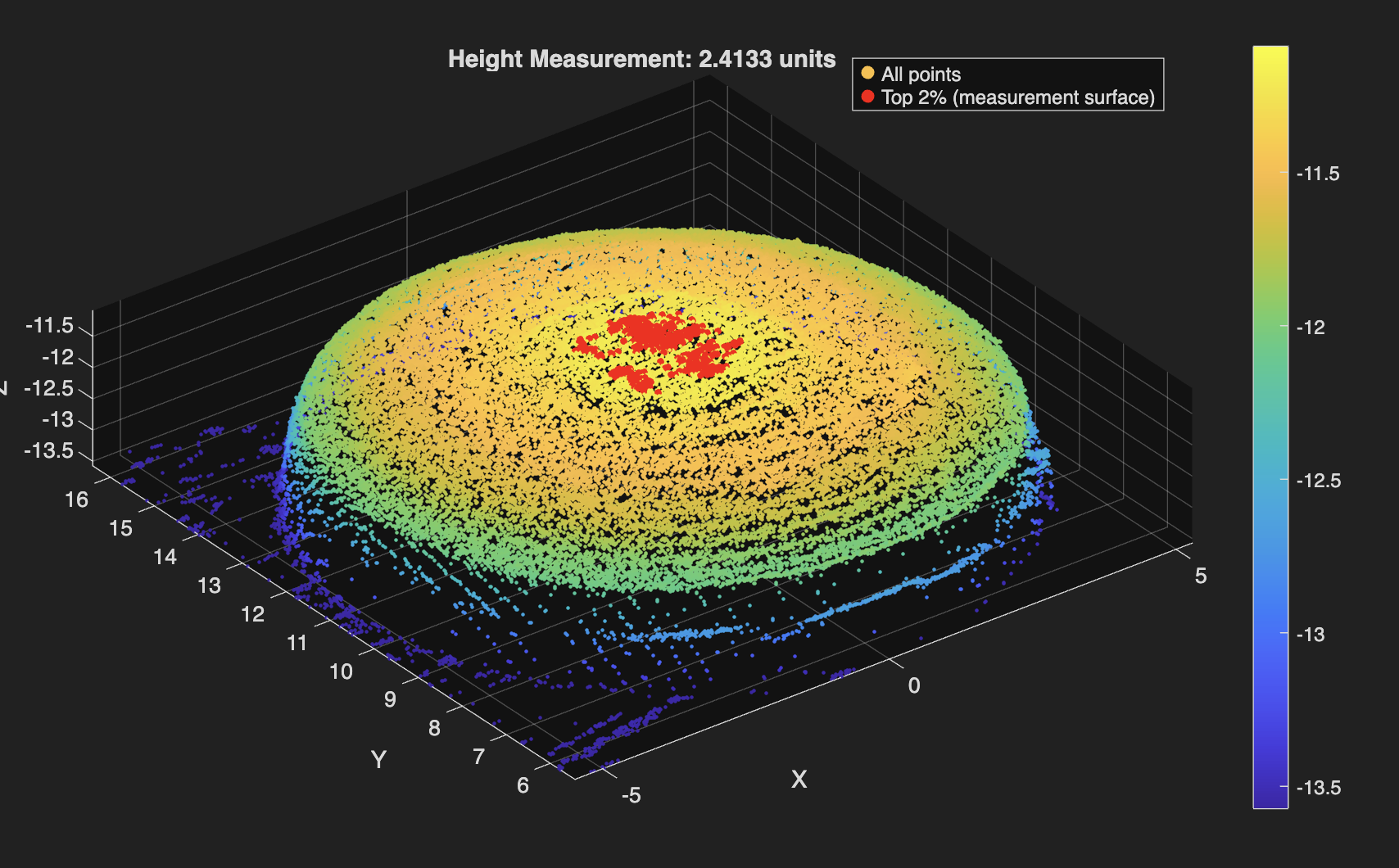
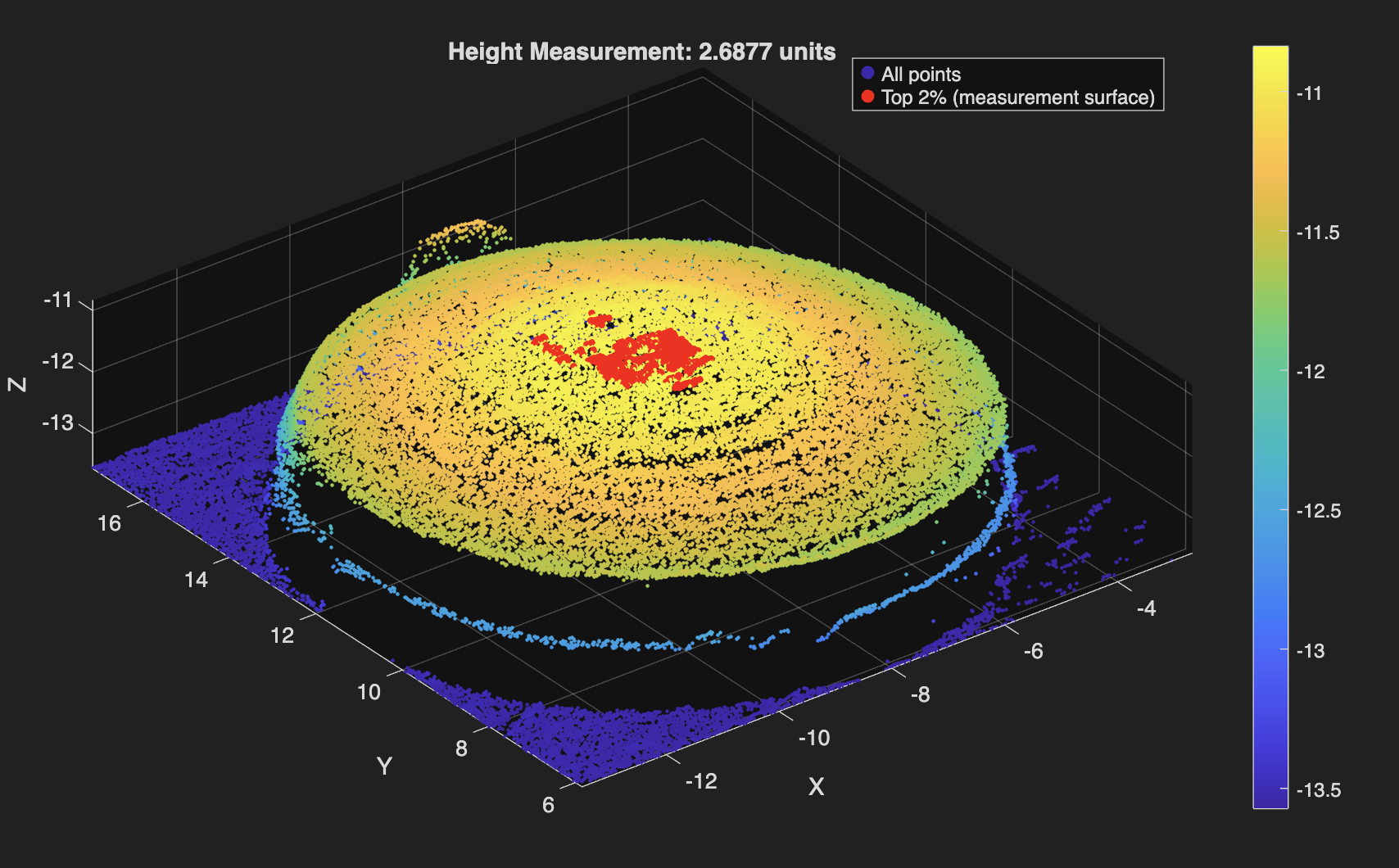
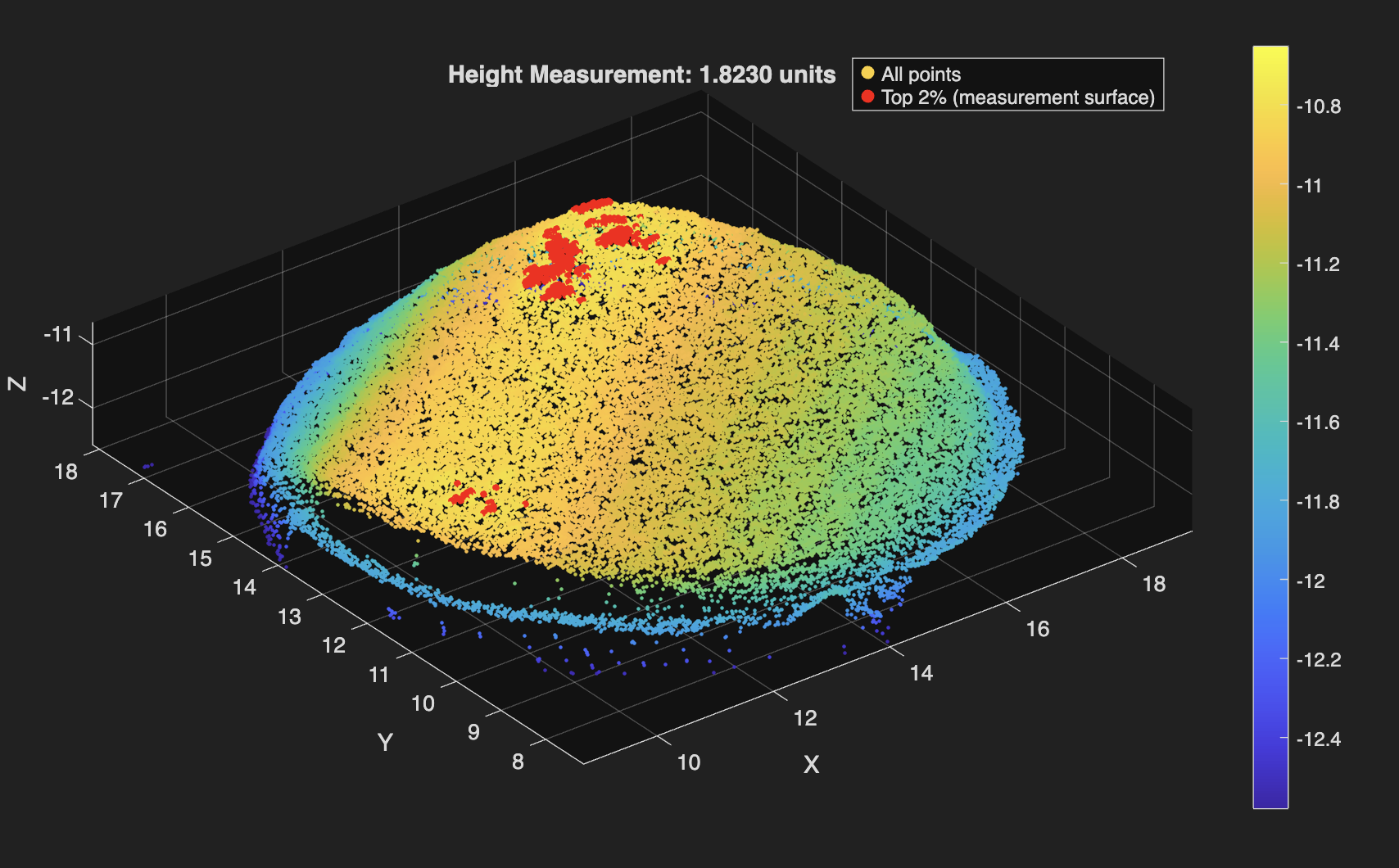
Used MATLAB to automate cartilage sample height calculations from CSV files exported by a custom-built laser scanner. Achieved less than 5% average error. Find the code below!
Raw laser scans are converted from CSV into structured (x,y,z) data, lightly downsampled to suppress noise, and referenced to a statistically defined platform surface identified via upper-percentile thresholding in the z-direction. Heights are extracted from the median of the top fraction (98th percentile) of points above this reference, which minimizes sensitivity to outliers and local surface artifacts, while an optional least-squares plane fit provides a geometric consistency check on the top surface. The code adapts automatically to scan resolution by adjusting percentile thresholds based on the number of points in the dataset, ensuring consistent behavior across varying scan densities. Importantly, the reported height error is not inferred solely from point-cloud variance but was calibrated empirically by averaging the deviation between measured heights and known heights of 3D-printed reference samples across dozens of independent scans, anchoring the uncertainty to repeatability.